Payload Information
General Information of This Payload
| Payload ID | PAY0XUVDV |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | SG2219 |
|||||
| Synonyms |
SG2219
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Target(s) | Human Deoxyribonucleic acid (hDNA) | |||||
| Structure |
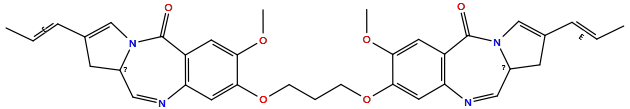
|
|||||
| Formula | C35H36N4O6 |
|||||
| Isosmiles | C/C=C/C1=CN2C(=O)c3cc(OC)c(OCCCOc4cc5c(cc4OC)C(=O)N4C=C(/C=C/C)CC4C=N5)cc3N=CC2C1 |
|||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C35H36N4O6/c1-5-8-22-12-24-18-36-28-16-32(30(42-3)14-26(28)34(40)38(24)20-22)44-10-7-11-45-33-17-29-27(15-31(33)43-4)35(41)39-21-23(9-6-2)13-25(39)19-37-29/h5-6,8-9,14-21,24-25H,7,10-13H2,1-4H3/b8-5+,9-6+
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
NFONWZNNBBUPNU-XVYDYJIPSA-N
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecule Weight |
608.695 |
Polar area |
102.26 |
||
Complexity |
45 |
xlogp Value |
6.3325 |
|||
Heavy Count |
45 |
Rot Bonds |
10 |
|||
Hbond acc |
8 |
Hbond Donor |
0 |
|||
The activity data of This Payload
| Standard Type | Value | Units | Cell line | Disease Model | Cell line ID | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 1 | pM |
K562 cells
|
Chronic myeloid leukemia
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 121 | pM |
SK-BR-3 cells
|
Breast adenocarcinoma
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 5 | pM |
NCI-N87 cells
|
Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 6.4 | pM |
MDA-MB-468 cells
|
Breast adenocarcinoma
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 641 | pM |
BT-474 cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[1] |
Each Antibody-drug Conjugate Related to This Payload
Full Information of The Activity Data of The ADC(s) Related to This Payload
Trastuzumab-SG3227 [Investigative]
Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Activity Date of This ADC | [2] | ||||
| Efficacy Data | Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) |
1.48 ng/mL
|
Low HER2 expression (HER2+) | ||
| Method Description |
The cytotoxic effect of Trastuzumab-SG3227 was assessed in cell viability assays for a diverse panel of human solid tumor cell lines representing breast and gastric cancers. The potency of Trastuzumab-SG3227 was assessed on the NCI-N87 cell line.
|
||||
| In Vitro Model | Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma | NCI-N87 cells | CVCL_1603 | ||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Activity Date of This ADC | [2] | ||||
| Efficacy Data | Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) |
2130.00 ng/mL
|
Negative expression (HER2-) | ||
| Method Description |
The cytotoxic effect of Trastuzumab-SG3227 was assessed in cell viability assays for a diverse panel of human solid tumor cell lines representing breast and gastric cancers. The potency of Trastuzumab-SG3227 was assessed on the MDA-MB-468 cell line.
|
||||
| In Vitro Model | Breast adenocarcinoma | MDA-MB-468 cells | CVCL_0419 | ||
Engineered HER-SG3227 [Investigative]
Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Activity Date of This ADC | [2] | ||||
| Efficacy Data | Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) |
4.29 ng/mL
|
Low HER2 expression (HER2+) | ||
| Method Description |
The cytotoxic effect of Engineered Her-SG3227 was assessed in cell viability assays for a diverse panel of human solid tumor cell lines representing breast and gastric cancers. The potency of Engineered Her-SG3227 was assessed on the NCI-N87 cell line.
|
||||
| In Vitro Model | Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma | NCI-N87 cells | CVCL_1603 | ||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Activity Date of This ADC | [2] | ||||
| Efficacy Data | Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) |
1220.00 ng/mL
|
Negative expression (HER2-) | ||
| Method Description |
The cytotoxic effect of Engineered Her-SG3227 was assessed in cell viability assays for a diverse panel of human solid tumor cell lines representing breast and gastric cancers. The potency of Engineered Her-SG3227 was assessed on the MDA-MB-468 cell line.
|
||||
| In Vitro Model | Breast adenocarcinoma | MDA-MB-468 cells | CVCL_0419 | ||
References
