Payload Information
General Information of This Payload
| Payload ID | PAY0ZZCOD |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Panobinostat |
|||||
| Synonyms |
Panobinostat; 404950-80-7; LBH589; LBH-589; Farydak; Panobinostat (LBH589); Faridak; LBH 589; (E)-N-Hydroxy-3-(4-(((2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)amino)methyl)phenyl)acrylamide; NVP-LBH589; NVP-LBH-589; Panobinostat [INN]; LBH-589B; Panobinostat(LBH589); Panobinostat [USAN:INN]; UNII-9647FM7Y3Z; (2E)-N-hydroxy-3-[4-({[2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]amino}methyl)phenyl]prop-2-enamide; CHEBI:85990; 9647FM7Y3Z; 404950-80-7 (free base); (E)-N-HYDROXY-3-(4-{[2-(2-METHYL-1H-INDOL-3-YL)-ETHYLAMINO]-METHYL}-PHENYL)-ACRYLAMIDE; (E)-N-hydroxy-3-[4-[[2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethylamino]methyl]phenyl]prop-2-enamide; Farydak (TN); (2E)-N-hydroxy-3-[4-({[2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]amino}methyl)phenyl]acrylamide; (2E)-N-Hydroxy-3-[4-[[[2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]amino]methyl]phenyl]-2-propenamide; 2-Propenamide, N-hydroxy-3-(4-(((2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)amino)methyl)phenyl)-, (2E)-; 2-Propenamide, N-hydroxy-3-[4-[[[2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]amino]methyl]phenyl]-, (2E)-; PANOBINOSTAT [MI]; LBH589 - Panobinostat; Panobinostat (USAN/INN); D0E3SH; PANOBINOSTAT [USAN]; N-Hydroxy-3-[4-[2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethylaminomethyl]phenyl]-2(E)-propenamide; PANOBINOSTAT [MART.]; MLS006011216; NVP-LBH 589; PANOBINOSTAT [WHO-DD]; SCHEMBL164801; SCHEMBL183197; CHEMBL483254; GTPL7489; SCHEMBL22773814; BDBM29589; CHEBI:93774; DTXSID40193506; EX-A169; FPOHNWQLNRZRFC-ZHACJKMWSA-N; N-hydroxy-3-[4-[[2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethylamino]methyl]phenyl]-2-propenamide; BCPP000187; BDBM198124; BCP01816; LBH58,9NVP-LBH589,Panobinostat; (LBH-589); MFCD09833242; NSC761190; s1030; AKOS005146046; BCP9000844; CCG-208762; CS-0267; DB06603; EX-8456; NSC-761190; (E)-3-[4-[[2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethylamino]methyl]phenyl]prop-2-enehydroxamic acid; (E)-N-hydroxy-3-(4-((2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethylamino)methyl)phenyl)acrylamide; Panobinostat, NVP-LBH589, LBH589; NCGC00263117-05; NCGC00263117-07; 2-Propenamide, N-hydroxy-3-(4-(((2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)amino) methyl)phenyl)-, (2E)-; AC-28652; AM808102; AS-17046; HY-10224; SMR004702978; SW219369-1; EC-000.2287; A25218; D10319; EN300-7395075; J-523585; Q7131441; BRD-K02130563-001-07-2; (E)-N-Hydroxy-3-[4-[[[2-(2-methyl-1H-indole-3-yl)ethyl]amino]methyl]phenyl]acrylamide; N-hydroxy-3 -[4-[[[2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]amino]methyl]phenyl]-2E-2-propenamide; N-hydroxy-3-[4-[[[2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]amino]methyl]phenyl]-2E-2-propenamide; Panobinostat;(E)-N-hydroxy-3-(4-((2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethylamino)methyl)phenyl)acrylamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Target(s) | Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) | |||||
| Structure |
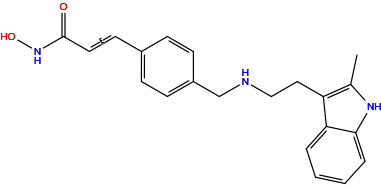
|
|||||
| Formula | C21H23N3O2 |
|||||
| Isosmiles | CC1=C(C2=CC=CC=C2N1)CCNCC3=CC=C(C=C3)/C=C/C(=O)NO |
|||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C21H23N3O2/c1-15-18(19-4-2-3-5-20(19)23-15)12-13-22-14-17-8-6-16(7-9-17)10-11-21(25)24-26/h2-11,22-23,26H,12-14H2,1H3,(H,24,25)/b11-10+
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
FPOHNWQLNRZRFC-ZHACJKMWSA-N
|
|||||
| IUPAC Name |
(E)-N-hydroxy-3-[4-[[2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethylamino]methyl]phenyl]prop-2-enamide
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecule Weight |
349.4 |
Polar area |
77.2 |
||
Complexity |
474 |
xlogp Value |
3 |
|||
Heavy Count |
26 |
Rot Bonds |
7 |
|||
Hbond acc |
3 |
Hbond Donor |
4 |
|||
The activity data of This Payload
| Standard Type | Value | Units | Cell line | Disease Model | Cell line ID | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 0.83 | nM |
HeLa cells
|
Endocervical adenocarcinoma
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 1 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[2] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 1.26 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 1.673 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[3] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 1.926 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[3] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 10.9 | nM |
CAL-27 cells
|
Tongue adenosquamous carcinom
|
[4] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | <100 | nM |
Hep-G2 cells
|
Hepatoblastoma
|
[5] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | <100 | nM |
CAL-148 cells
|
Breast carcinoma
|
[5] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 1000 | nM |
PANC-1 cells
|
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
|
[6] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >10000 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >10000 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 11 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[7] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 13 | nM |
Sf21 cells
|
Normal
|
[7] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 150 | nM |
KM3/BTZ cells
|
Multiple myeloma
|
[8] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 150.71 | nM |
A2780 cells
|
Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 169.5 | nM |
A2780 cells
|
Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 17.51 | nM |
NCI-H1975 cells
|
Lung adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 18 | nM |
COLO 205 cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[10] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 190.3 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >19952.62 | nM |
Vero C1008 cells
|
Normal
|
[11] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 2 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[2] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 2 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[2] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 2.059 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[3] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 2.097 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[3] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 2.1 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[7] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 2.1 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[3] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 2.27 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 2.5 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[7] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 2.97 | nM |
MV4-11 cells
|
Childhood acute monocytic leukemia
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 20 | nM |
A-549 cells
|
Lung adenocarcinoma
|
[5] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 20 | nM |
BC1 cells
|
Primary effusion lymphoma
|
[12] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 20.1 | nM |
KM3/BTZ cells
|
Multiple myeloma
|
[8] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 200 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[7] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >20000 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >20000 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >20000 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >20000 | nM |
Vero C1008 cells
|
Normal
|
[11] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 21.28 | nM |
Bel-7402 cells
|
Hepatoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 22 | nM |
HeLa cells
|
Endocervical adenocarcinoma
|
[13] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 231 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[2] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 24 | nM |
PC-3 cells
|
Prostate carcinoma
|
[10] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 2680 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[2] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 27.85 | nM |
EBC-1 cells
|
Lung squamous cell carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 280 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[7] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 2830 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[2] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 29.13 | nM |
MDA-MB-231 cells (5T4 overexpression)
|
Breast adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 3.28 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 3.36 | nM |
HCT 116 cells
|
Colon carcinoma
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 30 | nM |
HeLa cells
|
Endocervical adenocarcinoma
|
[14] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | <30 | nM |
MV4-11 cells
|
Childhood acute monocytic leukemia
|
[15] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 337.8 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 35 | nM |
A2780 cells
|
Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma
|
[10] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 37.55 | nM |
HT-29 cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 373 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[2] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 4.16 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 4.3 | nM |
HuT 78 cells
|
T lymphocytic leukemia
|
[16] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 4.45 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 4.86 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 4112 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 4354 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 46 | nM |
MED-MEB-8A cells
|
Medulloblastoma
|
[17] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 48 | nM |
HCT 116 cells
|
Colon carcinoma
|
[10] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 5.2 | nM |
MV4-11 cells
|
Childhood acute monocytic leukemia
|
[3] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 54 | nM |
UW228 cells
|
Medulloblastoma
|
[17] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 54.8 | nM |
A2780 cells
|
Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma
|
[4] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 6.98 | nM |
T-47D cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 67 | nM |
UW426 cells
|
Medulloblastoma
|
[17] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 7.67 | nM |
A2780 cells
|
Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma
|
[4] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 70 | nM |
NFF Fibroblast cells
|
Normal
|
Undisclosed | [18] |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 70 | nM |
NFF Fibroblast cells
|
Normal
|
Undisclosed | [19] |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 70 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[18] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 70 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[19] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 8.32 | nM |
A2780 cells
|
Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 8.42 | nM |
NCI-N87 cells
|
Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 887.8 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 9 | nM |
MCF7-F (fulvestrant resistant) cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 92 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[2] |
Each Antibody-drug Conjugate Related to This Payload
References
