Payload Information
General Information of This Payload
| Payload ID | PAY0KPOZO |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Genistein |
|||||
| Synonyms |
Genistein; 446-72-0; Prunetol; 4',5,7-Trihydroxyisoflavone; Genisterin; Genisteol; Sophoricol; 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one; 5,7,4'-Trihydroxyisoflavone; Bonistein; Genestein; Differenol A; NPI 031L; 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)chromen-4-one; 5,7-Dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one; 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-; C.I. 75610; SIPI 807-1; MFCD00016952; NSC 36586; CCRIS 7675; 4',5, 7-Trihydroxyisoflavone; 5,7-Dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-benzopyrone; NSC36586; EINECS 207-174-9; UNII-DH2M523P0H; NSC-36586; Genistein [USAN]; Lactoferrin-genistein; BRN 0263823; DH2M523P0H; NPI-031L; DTXSID5022308; ISOFLAVONE, 4',5,7-TRIHYDROXY-; CHEBI:28088; HSDB 7475; BIO-300; SIPI-807-1; CHEMBL44; FW-635I-2; Bio 300; PTI G4660 (Genistein); MLS000738127; DTXCID002308; STO514; PTI G4660; PTI-G4660; SIPI-9764-I; PTI-G 4660; 5-18-04-00594 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); TNP00151; Genistein (USAN); GENISTEIN (ENDOCRINE DISRUPTER); GEN; NCGC00015479-09; GENISTEIN (MART.); GENISTEIN [MART.]; G 6649; GENISTEIN (USP-RS); GENISTEIN [USP-RS]; 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-chromen-4-one; ENDOCRINE DISRUPTOR (GENISTEIN) (SEE ALSO GENISTEIN (446-72-0)); 690224-00-1; CAS-446-72-0; 4,5,7-Trihydroxyiso-flavone; SR-01000075498; 3kgt; 3kgu; 4′ Genistein, 8; Genistein,(S); Genistein (GEN); IN1327; Genistein (flavonoid); Spectrum_000320; Tocris-1110; 1x7r; 2qa8; Genistein 85% HPLC; GENISTEIN [INN]; SpecPlus_000305; GENISTEIN [MI]; GENISTEIN [HSDB]; GENISTEIN [INCI]; Spectrum2_000638; Spectrum3_000678; Spectrum4_001543; Spectrum5_000106; Lopac-G-6649; ,5,7-Trihydroxyisoflavone; 4',7-Trihydroxyisoflavone; D0L4FS; MolMap_000022; UPCMLD-DP096; G10000; GENISTEIN [WHO-DD]; 4,5,7-Trihydroxyisoflavone; Isoflavone,5,7-trihydroxy-; Lopac0_000520; Oprea1_224620; Oprea1_437815; SCHEMBL19166; BSPBio_002375; KBioGR_002006; KBioGR_002564; KBioSS_000800; KBioSS_002573; NPI031L; SPECTRUM210296; BIDD:ER0113; DivK1c_006401; Genistein, analytical standard; SPBio_000636; 4',5,7-Trihydroxy isoflavone; 4',5,7-trihydroxy-Isoflavone; GTPL2826; MEGxp0_000568; 4,5,7-Trihydroxy Iso-Flavone; UPCMLD-DP096:001; ACon1_001065; BDBM19459; C.I. 75610(ChemID); cid_5280961; KBio1_001345; KBio2_000800; KBio2_002564; KBio2_003368; KBio2_005132; KBio2_005936; KBio2_007700; KBio3_001595; KBio3_003042; CHEBI: 28088; cMAP_000086; Bio1_000445; Bio1_000934; Bio1_001423; HMS2271K09; HMS3261H21; HMS3267K14; HMS3412I13; HMS3428M01; HMS3649B22; HMS3654D17; HMS3676I13; HMS3742I07; AMY25676; BCP07581; Tox21_110161; Tox21_201428; Tox21_300585; Tox21_500520; AC-472; BBL010484; CCG-38551; HB2775; LMPK12050218; s1342; STK801619; WHO 11073; AKOS001590147; Tox21_110161_1; CS-1534; CS-O-01020; DB01645; KS-5128; LP00520; LS-1266; SB17235; SDCCGSBI-0050503.P003; SMP1_000133; Genistein; 4',5,7-Trihydroxyisoflavone; NCGC00015479-01; NCGC00015479-02; NCGC00015479-04; NCGC00015479-05; NCGC00015479-06; NCGC00015479-07; NCGC00015479-08; NCGC00015479-10; NCGC00015479-11; NCGC00015479-12; NCGC00015479-13; NCGC00015479-14; NCGC00015479-15; NCGC00015479-16; NCGC00015479-17; NCGC00015479-18; NCGC00015479-19; NCGC00015479-20; NCGC00015479-38; NCGC00025005-01; NCGC00025005-02; NCGC00025005-03; NCGC00025005-04; NCGC00025005-05; NCGC00025005-06; NCGC00025005-07; NCGC00169711-01; NCGC00169711-02; NCGC00254275-01; NCGC00258979-01; NCGC00261205-01; HY-14596; NCI60_003369; SMR000112580; SY050124; EU-0100520; FT-0603395; FT-0668961; FT-0668962; G0272; GENISTEIN (CONSTITUENT OF RED CLOVER); SW203763-2; C06563; D11680; EN300-210743; G-2535; Genistein, synthetic, >=98% (HPLC), powder; K00046; US8552057, 2; AB00052696_09; AB00052696_12; A826657; GENISTEIN (CONSTITUENT OF SOY ISOFLAVONES); Q415957; GENISTEIN (CONSTITUENT OF RED CLOVER) [DSC]; Genistein, primary pharmaceutical reference standard; Q-100484; SR-01000075498-1; SR-01000075498-3; SR-01000075498-6; 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5,7-bis(oxidanyl)chromen-4-one; 4 inverted exclamation marka,5,7-Trihydroxyisoflavone; BRD-K43797669-001-02-3; BRD-K43797669-001-03-1; BRD-K43797669-001-10-6; Genistein, from Glycine max (soybean), ~98% (HPLC); SR-01000075498-10; 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-benzopyran-4-one; F0001-2388; GENISTEIN (CONSTITUENT OF SOY ISOFLAVONES) [DSC]; 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-; 4h-1-benzopiran-4-ona, 5,7-dihidroxi-3-(4-hidroxifenil)-; 5,7-Dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4 H-1-benzopyran-4-one; Genistein, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-(ChemID); Genistein, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Target(s) | Pro-epidermal growth factor (EGF) | |||||
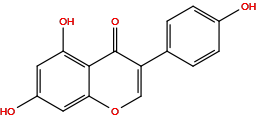
| Structure |
|
|||||
| Formula | C15H10O5 |
|||||
| Isosmiles | [H]Oc1c([H])c([H])c(-c2c([H])oc3c([H])c(O[H])c([H])c(O[H])c3c2=O)c([H])c1[H] |
|||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C15H10O5/c16-9-3-1-8(2-4-9)11-7-20-13-6-10(17)5-12(18)14(13)15(11)19/h1-7,16-18H
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
TZBJGXHYKVUXJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||||
| IUPAC Name |
5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)chromen-4-one
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecule Weight |
270.24 |
Polar area |
90.9 |
||
Complexity |
270.0528234 |
xlogp Value |
2.5768 |
|||
Heavy Count |
20 |
Rot Bonds |
4 |
|||
Hbond acc |
5 |
Hbond Donor |
3 |
|||
The activity data of This Payload
| Standard Type | Value | Units | Cell line | Disease Model | Cell line ID | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 0.1 | ug/mL |
A-431 cells
|
Skin squamous cell carcinoma
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 0.54 | ug/mL |
Neutrophil cells
|
Normal
|
Undisclosed | [2] |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 0.7 | ug/mL |
A-431 cells
|
Skin squamous cell carcinoma
|
[1] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 13.9 | ug/mL |
C8166 cells
|
Leukemia
|
[3] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 4.18 | ug/mL |
B16-BL6 cells
|
Melanoma
|
[4] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 6.99 | ug/mL |
Neutrophil cells
|
Normal
|
Undisclosed | [2] |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 1.3 | nM |
HEK-293T cells
|
Normal
|
[5] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 1.7 | nM |
SH-SY5Y cells
|
Bone marrow neuroblastoma
|
[6] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 1000 | nM |
MCF7-F (fulvestrant resistant) cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[7] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >1000 | nM |
RAW264.7 cells
|
Monocytic-macrophage leukemia
|
[8] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 10000 | nM |
CCRF-CEM cells
|
T acute lymphoblastic leukemia
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 10000 | nM |
LNCaP cells
|
Prostate carcinoma
|
[10] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 10000 | nM |
MCF7-F (fulvestrant resistant) cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[11] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
PC-3 cells
|
Prostate carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
K-562 cells
|
Chronic myelogenous leukemia
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >100000 | nM |
U-937 cells
|
Adult acute monocytic leukemia
|
[12] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
U-251MG cells
|
Astrocytoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >100000 | nM |
Caco-2 cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[13] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >100000 | nM |
Hep-G2 cells
|
Hepatoblastoma
|
[14] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >100000 | nM |
DU145 cells
|
Prostate carcinoma
|
[15] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
COLO 205 cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
HT-29 cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
MDA-MB-435 cells
|
Amelanotic melanoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
SK-MEL-28 cells (BRAF inhibitor resistant)
|
Cutaneous melanoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
SK-MEL-5 cells
|
Cutaneous melanoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
T-47D cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
NCI-ADR-RES cells
|
High grade ovarian serous adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
NCI-H23 cells
|
Lung adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
OVCAR-5 cells
|
Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
OVCAR-8 cells
|
High grade ovarian serous adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
SF539 cells
|
Gliosarcoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
SF268 cells
|
Astrocytoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
MCF7-F (fulvestrant resistant) cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >100000 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[16] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >100000 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[17] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
HCC 2998 cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
HOP-92 cells
|
Non-small cell lung carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
KM12 cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
M14 cells
|
Melanoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
Malme-3M cells
|
Melanoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
OVCAR-4 cells
|
Ovarian adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
TK-10 cells
|
Renal carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
UACC-62 cells
|
Melanoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 100000 | nM |
MDA-N cells
|
Breast carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >100000 | nM |
L02 cells
|
Cervical carcinoma
|
[14] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 10469 | nM |
Farage cells
|
Normal
|
[18] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 108000 | nM |
A-431 cells
|
Skin squamous cell carcinoma
|
[19] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 10924 | nM |
U-937 cells
|
Adult acute monocytic leukemia
|
[18] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 11000 | nM |
MCF7-F (fulvestrant resistant) cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[20] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 11000 | nM |
Ventricular myocyte cells
|
Normal
|
Undisclosed | [21] |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 11000 | nM |
Ventricular myocyte cells
|
Normal
|
Undisclosed | [22] |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 11013 | nM |
Platelet cells
|
Normal
|
Undisclosed | [18] |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 1110 | nM |
Neutrophil cells
|
Normal
|
Undisclosed | [23] |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 11400 | nM |
RAW264.7 cells
|
Monocytic-macrophage leukemia
|
[24] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 1300000 | nM |
MDA-kb2 cells
|
Breast adenocarcinoma
|
[25] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 135 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[18] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 14200 | nM |
FRT cells
|
Normal
|
[26] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 14400 | nM |
Huh-7 cells
|
Adult hepatocellular carcinoma
|
[27] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 14910 | nM |
Farage cells
|
Normal
|
[18] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 15100 | nM |
MCF7-F (fulvestrant resistant) cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[28] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 15848.93 | nM |
SNB-75 cells
|
Glioblastoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 16500 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[30] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 16918 | nM |
Farage cells
|
Normal
|
[18] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 16982.44 | nM |
NCI-ADR-RES cells
|
High grade ovarian serous adenocarcinoma
|
[31] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 17000 | nM |
MDA-MB-436 cells
|
Metastasis of ductal carcinoma
|
[11] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 17442 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[18] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 17560 | nM |
K-562 cells
|
Chronic myelogenous leukemia
|
[32] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 17782.79 | nM |
NCI-H522 cells
|
Non-small cell lung carcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 18100 | nM |
RAW cells
|
Monocytic-macrophage leukemia
|
Undisclosed | [33] |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 18197.01 | nM |
LOX IMVI cells
|
Melanoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 183900 | nM |
BALB/3T3 cells
|
Normal
|
[34] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 19.95 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[35] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 19100 | nM |
RAW264.7 cells
|
Monocytic-macrophage leukemia
|
[36] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 19498.45 | nM |
ACHN cells
|
Renal adenocarcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 19904 | nM |
CHO cells
|
Normal
|
[18] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >19952.62 | nM |
Vero C1008 cells
|
Normal
|
[37] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 2.88 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[18] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 20000 | nM |
Huh-7 cells
|
Adult hepatocellular carcinoma
|
[38] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 20000 | nM |
Ventricular myocyte cells
|
Normal
|
Undisclosed | [21] |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >20000 | nM |
Vero C1008 cells
|
Normal
|
[37] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 21877.62 | nM |
DMS-273 cells
|
Small cell lung carcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 21877.62 | nM |
MCF-12A cells
|
Normal
|
[31] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 22000 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[39] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 2210 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[30] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 240 | nM |
Ishikawa cells
|
Endometrial adenocarcinoma
|
[40] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 24000 | nM |
LNCaP cells
|
Prostate carcinoma
|
[10] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 24000 | nM |
NIH3T3 cells
|
Normal
|
[28] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 24800 | nM |
Hep-G2 cells
|
Hepatoblastoma
|
[41] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 24945.95 | nM |
UO-31 cells
|
Renal carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 25118.86 | nM |
HCT 116 cells
|
Colon carcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 25118.86 | nM |
MKN-1 cells
|
Gastric carcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 25120 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[16] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 2520 | nM |
BTI-TN-5B1-4 cells
|
Normal
|
[18] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 26000 | nM |
MCF7-F (fulvestrant resistant) cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[42] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 26000 | nM |
RAW264.7 cells
|
Monocytic-macrophage leukemia
|
[43] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 26302.68 | nM |
A-549 cells
|
Lung adenocarcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 26302.68 | nM |
NCI-H460 cells
|
Lung large cell carcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 26302.68 | nM |
SF539 cells
|
Gliosarcoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 26500 | nM |
RAW264.7 cells
|
Monocytic-macrophage leukemia
|
[44] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 26915.35 | nM |
NCI-ADR-RES cells
|
High grade ovarian serous adenocarcinoma
|
[31] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 26915.35 | nM |
HBC-5 cells
|
Breast carcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 27542.29 | nM |
NCI-H226 cells
|
Pleural epithelioid mesothelioma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 27700 | nM |
WiDr cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[28] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 278000 | nM |
A-431 cells
|
Skin squamous cell carcinoma
|
[19] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 28400 | nM |
BV-2 cells
|
Normal
|
[45] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 28840.32 | nM |
SF-295 cells
|
Glioblastoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 29.4 | nM |
HEK-293T cells
|
Normal
|
[5] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 29200 | nM |
NHEM693 cells
|
Normal
|
[46] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 29716.66 | nM |
ACHN cells
|
Renal adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 30000 | nM |
BxPC-3 CDX model cells
|
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
|
[47] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >30000 | nM |
MCF7-F (fulvestrant resistant) cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[42] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 30000 | nM |
Sf9 cells
|
Normal
|
[17] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 30199.52 | nM |
HCT 15 cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 30199.52 | nM |
MKN7 cells
|
Gastric tubular adenocarcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 30199.52 | nM |
SF268 cells
|
Astrocytoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 30199.52 | nM |
MCF-12A cells
|
Normal
|
[31] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 30650 | nM |
LNCaP cells
|
Prostate carcinoma
|
[13] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 31000 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[39] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 31622.78 | nM |
OVCAR-3 cells (FZD7 overexpression)
|
Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 32359.37 | nM |
MKN45 cells
|
Gastric adenocarcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 32359.37 | nM |
NCI-ADR-RES cells
|
High grade ovarian serous adenocarcinoma
|
[31] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 32359.37 | nM |
MCF-12A cells
|
Normal
|
[31] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 32900 | nM |
Vero cells
|
Normal
|
[48] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 34900 | nM |
HCT 116 cells
|
Colon carcinoma
|
[13] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 35481.34 | nM |
OVCAR-8 cells
|
High grade ovarian serous adenocarcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 35695.8 | nM |
UoC-B1 cells
|
B acute lymphoblastic leukemia
|
[49] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 36000 | nM |
SK-MEL-2 cells (MEK inhibitor-resistant)
|
Melanoma
|
[50] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 36307.81 | nM |
NCI-H23 cells
|
Lung adenocarcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 36307.81 | nM |
MKN-74 cells
|
Stomach adenocarcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 36391.5 | nM |
NCI-H522 cells
|
Non-small cell lung carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 37153.52 | nM |
MDA-MB-231 cells (5T4 overexpression)
|
Breast adenocarcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 37400 | nM |
LNCaP cells
|
Prostate carcinoma
|
[15] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 3890.45 | nM |
CHO cells
|
Normal
|
[51] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 38904.51 | nM |
LNCaP cells
|
Prostate carcinoma
|
[31] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 38904.51 | nM |
SNB-78 cells
|
Glioblastoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 39810.72 | nM |
MKN-28 cells
|
Gastric epithelial carcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 4.1 | nM |
HeLa cells
|
Endocervical adenocarcinoma
|
[6] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 403000 | nM |
SK-BR-3 cells
|
Breast adenocarcinoma
|
[19] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 40364.54 | nM |
MOLT-4 cells
|
Adult T acute lymphoblastic leukemia
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 40738.03 | nM |
RXF 631 cells
|
Renal carcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 41670 | nM |
AGS cells
|
Gastric adenocarcinoma
|
[13] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 41975.9 | nM |
NCI-H460 cells
|
Lung large cell carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 42657.95 | nM |
PC-3 cells
|
Prostate carcinoma
|
[31] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 42657.95 | nM |
U-251MG cells
|
Astrocytoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 42657.95 | nM |
MCF7-F (fulvestrant resistant) cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 43000 | nM |
MDA-MB-231 cells (5T4 overexpression)
|
Breast adenocarcinoma
|
[50] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 43090 | nM |
A-549 cells
|
Lung adenocarcinoma
|
[13] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 43151.91 | nM |
786-O cells
|
Renal cell carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 43651.58 | nM |
OVCAR-4 cells
|
Ovarian adenocarcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 43651.58 | nM |
BSY-1 cells
|
Breast carcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 43651.58 | nM |
HBC-4 cells
|
Breast carcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 4400 | nM |
NIH3T3 cells
|
Normal
|
[52] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 44000 | nM |
LN-229 cells
|
Glioblastoma
|
[50] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 45200 | nM |
Hepa-1c1c7 cells
|
Hepatocellular carcinoma of the mouse
|
[53] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 45708.82 | nM |
MCF7-F (fulvestrant resistant) cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[31] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 45708.82 | nM |
HCC 2998 cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 46000 | nM |
BT-20 cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type
|
[47] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 46773.51 | nM |
St-4 cells
|
Stomach carcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 47000 | nM |
NCI-H460 cells
|
Lung large cell carcinoma
|
[50] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 47290 | nM |
DU145 cells
|
Prostate carcinoma
|
[13] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 48 | nM |
HeLa cells
|
Endocervical adenocarcinoma
|
[6] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 48000 | nM |
U-937 cells
|
Adult acute monocytic leukemia
|
[12] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 48000 | nM |
T-47D cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[50] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 48977.88 | nM |
DMS 114 cells
|
Lung small cell carcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 49203.95 | nM |
SW620 cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 50000 | nM |
PC-3 cells
|
Prostate carcinoma
|
[47] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 50000 | nM |
HT-29 cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[50] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 50000 | nM |
COLO357 cells
|
Pancreatic carcinoma
|
[47] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >50000 | nM |
RAW264.7 cells
|
Monocytic-macrophage leukemia
|
[54] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | >500000 | nM |
Melan-a cells
|
Normal
|
[55] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 501.19 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[35] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 50118.72 | nM |
DU145 cells
|
Prostate carcinoma
|
[31] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 50118.72 | nM |
OVCAR-5 cells
|
Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 50118.72 | nM |
KM12 cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 510 | nM |
Ishikawa cells
|
Endometrial adenocarcinoma
|
[56] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 52480.75 | nM |
SN12C cells
|
Renal cell carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 52480.75 | nM |
MCF7-F (fulvestrant resistant) cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[31] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 52780 | nM |
HT-29 cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[13] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 53703.18 | nM |
HT-29 cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 54954.09 | nM |
SF-295 cells
|
Glioblastoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 55000 | nM |
U-87MG ATCC cells
|
Glioblastoma
|
[50] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 56754.46 | nM |
SR cells
|
Leukemia
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 57500 | nM |
Cardiac Muscle cells
|
Normal
|
Undisclosed | [22] |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 57830 | nM |
Melan-a cells
|
Normal
|
[55] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 58180 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[16] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 59338 | nM |
SEM cells
|
Leukemia
|
[49] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 61.33 | nM |
SF-126 cells
|
Glioblastoma
|
||
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 61659.5 | nM |
MCF7-F (fulvestrant resistant) cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[31] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 6170 | nM |
FRT cells
|
Normal
|
[26] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 62373.48 | nM |
A-549 cells
|
Lung adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 62710 | nM |
MCF7-F (fulvestrant resistant) cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[13] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 63095.73 | nM |
EKVX cells
|
Non-small cell lung carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 64000 | nM |
A-549 cells
|
Lung adenocarcinoma
|
[50] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 65000 | nM |
LNCaP cells
|
Prostate carcinoma
|
[57] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 65162.84 | nM |
Hs 578T cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 65170 | nM |
PC-3 cells
|
Prostate carcinoma
|
[13] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 6720 | nM |
Neutrophil cells
|
Normal
|
Undisclosed | [58] |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 67694.5 | nM |
Hep-G2 cells
|
Hepatoblastoma
|
[49] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 67990 | nM |
HEK293 cells
|
Normal
|
[16] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 68600 | nM |
PC-3 cells
|
Prostate carcinoma
|
[15] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 690 | nM |
Neutrophil cells
|
Normal
|
Undisclosed | [58] |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 6900 | nM |
MDCK cells
|
Normal
|
[59] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 69823.24 | nM |
HL-60 cells
|
Adult acute myeloid leukemia
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 7000 | nM |
FRT cells
|
Normal
|
[60] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 71614.34 | nM |
IGROV-1 cells
|
Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 72000 | nM |
U-937 cells
|
Adult acute monocytic leukemia
|
[12] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 72945.75 | nM |
HCT 15 cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 73 | nM |
HeLa cells
|
Endocervical adenocarcinoma
|
[61] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 73000 | nM |
COLO 201 cells
|
Colon adenocarcinoma
|
[50] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 74131.02 | nM |
NCI-H226 cells
|
Pleural epithelioid mesothelioma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 77000 | nM |
MCF7-F (fulvestrant resistant) cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[20] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 7720 | nM |
Platelet cells
|
Normal
|
Undisclosed | [18] |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 77803.66 | nM |
RPMI-8226 cells
|
Plasma cell myeloma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 79000 | nM |
BxPC-3 CDX model cells
|
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
|
[50] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 79210 | nM |
B16-F10 cells
|
Mouse melanoma
|
[4] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 8000 | nM |
ANN-1 cells
|
Normal
|
[28] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 8200 | nM |
CHO cells
|
Normal
|
[26] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 8480 | nM |
CHO cells
|
Normal
|
[26] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | >86206.9 | nM |
SUP-B15 cells
|
B-lymphoblastic leukemia
|
[49] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | >86206.9 | nM |
KOPN-8 cells
|
Leukemia
|
[49] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | >86206.9 | nM |
BJ cells
|
Normal
|
[49] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 87000 | nM |
PANC-1 cells
|
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
|
[50] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 8800 | nM |
MCF7-F (fulvestrant resistant) cells
|
Invasive breast carcinoma
|
[59] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 88000 | nM |
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells(HUVEC)
|
Normal
|
Undisclosed | [62] |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 88307.99 | nM |
BT-549 cells
|
Breast ductal carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 89125.09 | nM |
SK-OV-3 cells (FZD7 overexpression)
|
Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma
|
[29] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 89410 | nM |
T98G cells
|
Glioblastoma
|
[13] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 9100 | nM |
Balb/MK cells
|
Normal
|
[63] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 9120.11 | nM |
CHO cells
|
Normal
|
[51] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 92044.96 | nM |
SNB-19 cells
|
Astrocytoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Cell Growth Inhibitory Concentration (GI50) | 92469.82 | nM |
DU145 cells
|
Prostate carcinoma
|
[9] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 956 | nM |
HeLa cells
|
Endocervical adenocarcinoma
|
[61] | |
| Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | 96700 | nM |
SK-BR-3 cells
|
Breast adenocarcinoma
|
[13] | |
| Half Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50) | 97000 | nM |
SK-BR-3 cells
|
Breast adenocarcinoma
|
[19] |
Each Antibody-drug Conjugate Related to This Payload
References
